Constructing a Risk-Free Curve Using Namibian Government Bonds: A Key Tool in Financial Valuation

Introduction
The concept of a risk-free curve is foundational in finance, serving as a benchmark for valuing a wide array of financial instruments, pension liabilities, and life insurance contracts. In Namibia, constructing an accurate risk-free curve using Namibian Government Bonds is essential for ensuring the precision and reliability of financial valuations, as mandated by various international accounting standards such as IAS 19 and IFRS 13. This article delves into the process of constructing a risk-free curve using Namibian Government Bonds, highlighting its importance and applications in the financial landscape.
Understanding the Risk-Free Curve
A risk-free curve is a graphical representation of the yields of hypothetical risk-free zero-coupon bonds over different maturities. In practice, government bonds are typically used as proxies for risk-free instruments, given their low default risk. The selection of these bonds is guided by their liquidity, maturity, and the alignment with South African Government Benchmark Bonds, which serve as a comparative benchmark. The Prudential Authority (PA) of the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) constructs a risk-free curve using South African Government Bonds monthly, which is widely utilised by life insurance companies and pension funds for liability valuation. Following a similar methodology, Namibia can construct its own risk-free curve using its government bonds.
Methodology for Constructing the Risk-Free Curve
The construction of the risk-free curve in Namibia involves several key steps:
Selection of Government Bonds: Namibian Government Bonds are chosen based on their liquidity, maturity, and alignment with South African Government Benchmark Bonds. This alignment ensures that the constructed curve reflects regional market dynamics. The GC27, GC30, GC32, GC35, GC37, GC43 and GC48 Bonds constitute the final set of Namibian Government Bonds used to construct the risk-free curve as at 31 July 2024 as shown below:
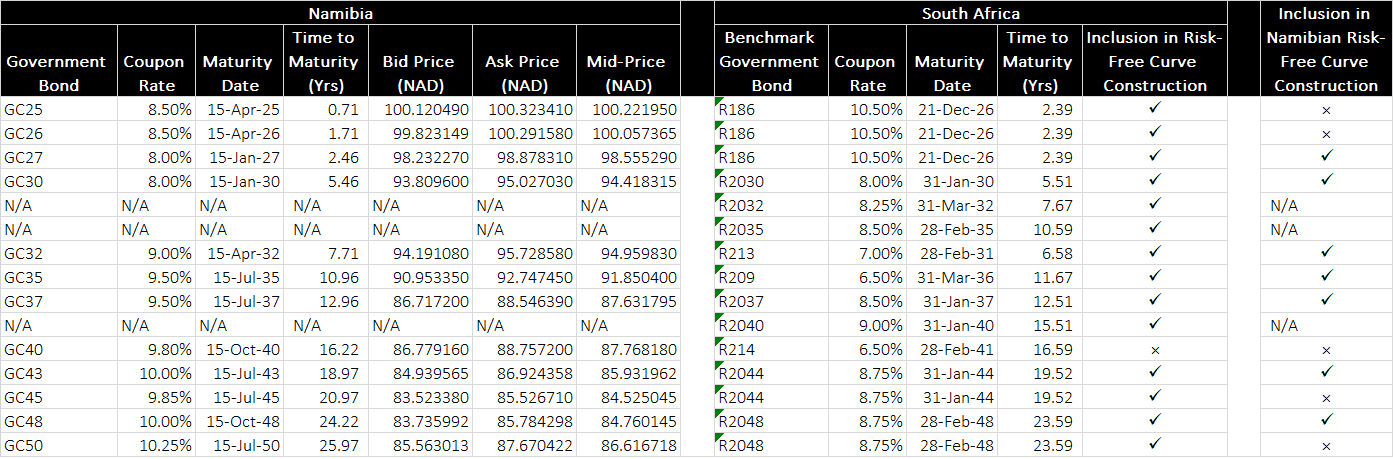
Data Collection: Information such as bid and ask prices, coupon rates, and maturity dates of the selected bonds is gathered. The mid-price is calculated to derive the zero-coupon yields.
Risk-free Curve Creation: The selected bonds are bootstrapped according to their terms using mid-prices and Piecewise Spline Cubic Interpolation to derive the zero-coupon yields and this ensures that the resulting zero curve can re-price all the instruments used in its creation. The zero-coupon yields are plotted against their respective maturities to form the risk-free curve.
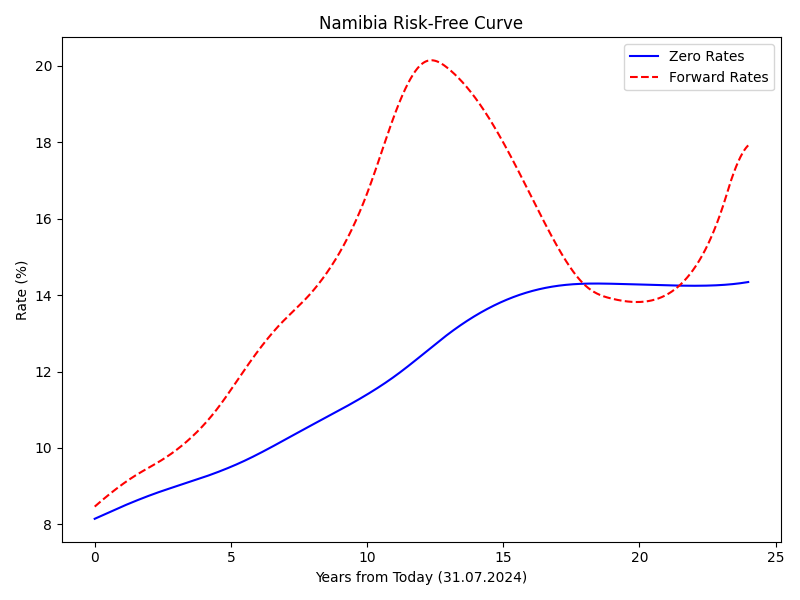
The graph below shows the risk-free curve (zero rates) in blue, and the forward curve determined from the zero curve in red dashed lines. The zero curve represents the yields of hypothetical risk-free zero-coupon bonds across different maturities, while the forward curve provides a projection of future interest rates.
Importance of the Risk-Free Curve
The risk-free curve plays a pivotal role in several key areas of financial management:
- Valuation of Financial Instruments: Under IFRS 13, the fair value measurement of financial instruments often relies on the discounting of future cash flows using the risk-free rate. An accurate risk-free curve ensures that the valuation reflects the current market conditions and provides a true and fair view of the financial position of the entity.
- Pension Liabilities: IAS 19 mandates that the discount rate used to measure the present value of defined benefit pension obligations should be determined by reference to market yields on high-quality corporate bonds or, in the absence of a deep market, government bonds. In Namibia, the risk-free curve constructed using Namibian Government Bonds serves as the benchmark for this purpose, directly impacting the valuation of pension liabilities.
- Life Insurance: For life insurance companies, the risk-free curve is used to discount future policyholder liabilities. This is critical in ensuring that the liabilities are accurately matched with the expected returns on assets, thus maintaining the solvency and financial stability of the insurance company.
- Financial Reporting: In financial reporting, the use of a risk-free curve is crucial in ensuring that the valuation of liabilities and assets is consistent with the principles of fair value and present value. This, in turn, affects the financial statements and the perceived financial health of the entity.
Regulatory References and Compliance
The construction and application of a risk-free curve in Namibia must align with international accounting standards to ensure compliance and accuracy in financial reporting. Key regulations include:
IFRS 13 – Fair Value Measurement: This standard emphasises the use of market-based inputs, including the risk-free rate, in determining the fair value of financial instruments. A well-constructed risk-free curve ensures that the fair value reflects current market conditions.
IAS 19 – Employee Benefits: This standard requires the use of high-quality corporate bonds or government bonds to determine the discount rate for pension liabilities. In the Namibian context, the risk-free curve constructed from government bonds serves as the reference rate for this purpose.
Conclusion
The construction of a risk-free curve using Namibian Government Bonds is not just a technical exercise; it is a critical component of the financial valuation process. Whether for valuing financial instruments, pension liabilities, or insurance contracts, the accuracy and reliability of the risk-free curve have far-reaching implications for financial stability and reporting in Namibia. By aligning with international standards like IAS 19 and IFRS 13, Namibian entities can ensure that their financial valuations are robust, compliant, and reflective of the true economic conditions.
The use of Namibian Government Bonds, carefully selected and benchmarked against South African Government Bonds, ensures that the risk-free curve constructed is not only relevant to the Namibian market but also consistent with regional financial practices. This alignment is crucial in maintaining the integrity and comparability of financial valuations across borders, ultimately contributing to the stability and transparency of the financial system in Namibia.

